Since UI.Vision RPA Version 4 and later we changed the macro storage from local storage to the chrome.fileSystem API:
Use the chrome.fileSystem API to create, read, navigate, and write to the user’s local file system. With this API, Chrome Apps can read and write to a user-selected location. For example, a text editor app can use the API to read and write local documents. All failures are notified via chrome.runtime.lastError.
We made this change to add folder support.
chrome.fileSystem stores all files a special location on the user’s hard drive where Chrome itself manages the files. We still call this “Local Storage” since everything is managed by the browser extension, and once you uninstall the extension the data is gone - just like with the “real” Local Storage. Thus chrome.fileSystem should not be confused with the hard-drive mode (XModules) storage mode that allows you to store macros on the normal file system.
![]() How to view the files stored by
How to view the files stored by chrome.fileSystem:
The easiest way is to go the the extension page, find the UI.Vision RPA extension, click on its background.html link, and then open the developer tools.
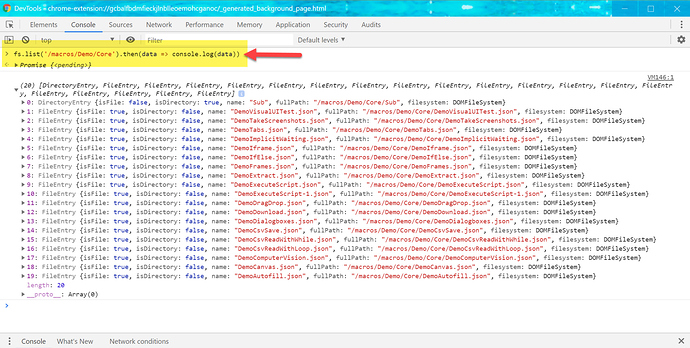
In the developer tools, go to “Console” and type:
fs.list('/macros/Demo/Core').then(data => console.log(data))
and voilà, there is the data:
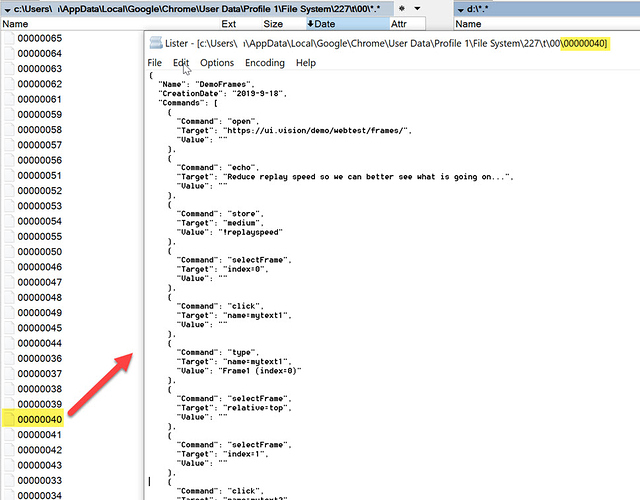
You also find the data deep inside Google Chrome’s appdata folder with any file explorer software (e. g. Windows File Explorer or Total Commander). The exact location is of course different between Windows, macOS and Linux. The screenshot below shows Windows:
PS: I updated the local storage page with a comment about the chrome.fileSystem and a link to this answer.